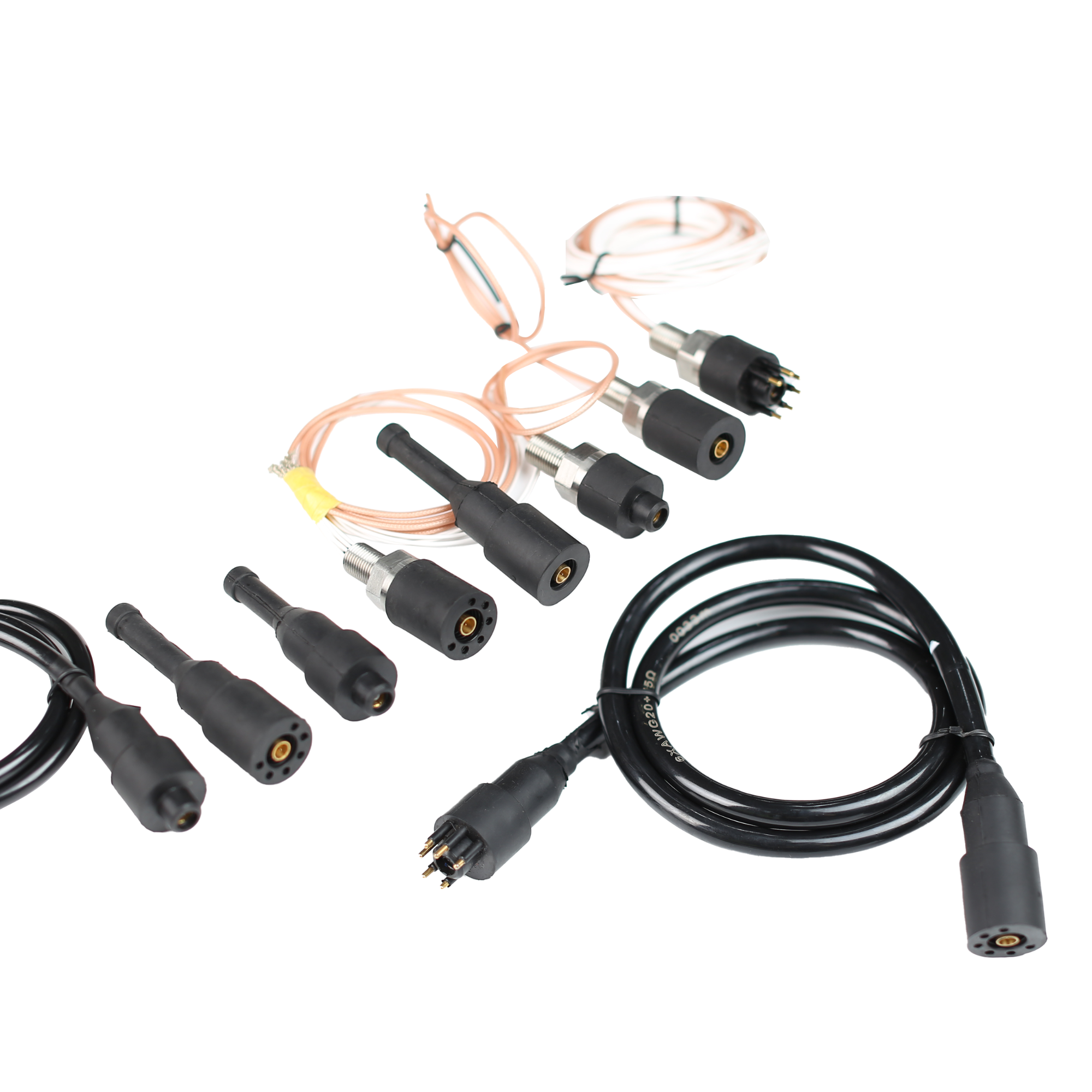
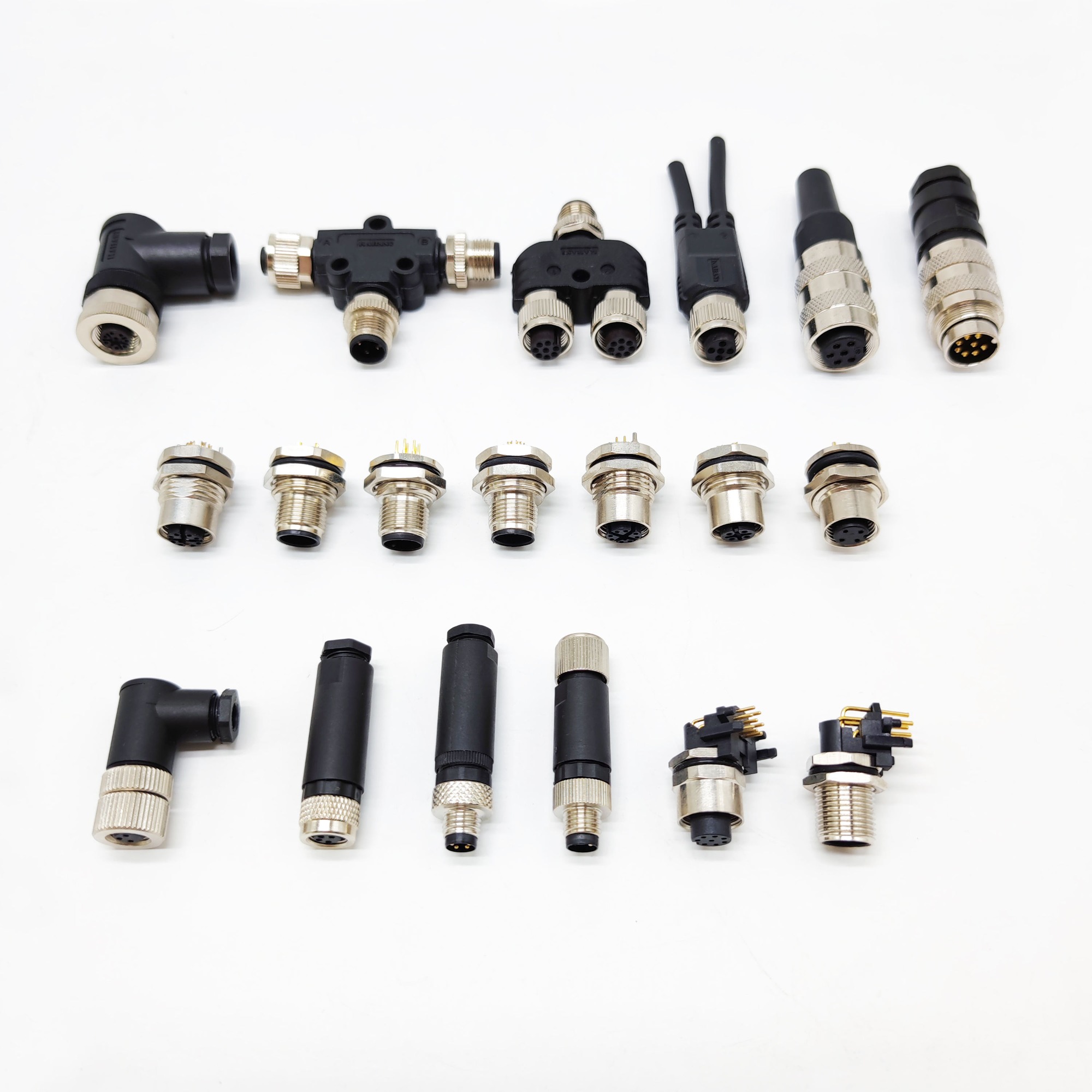
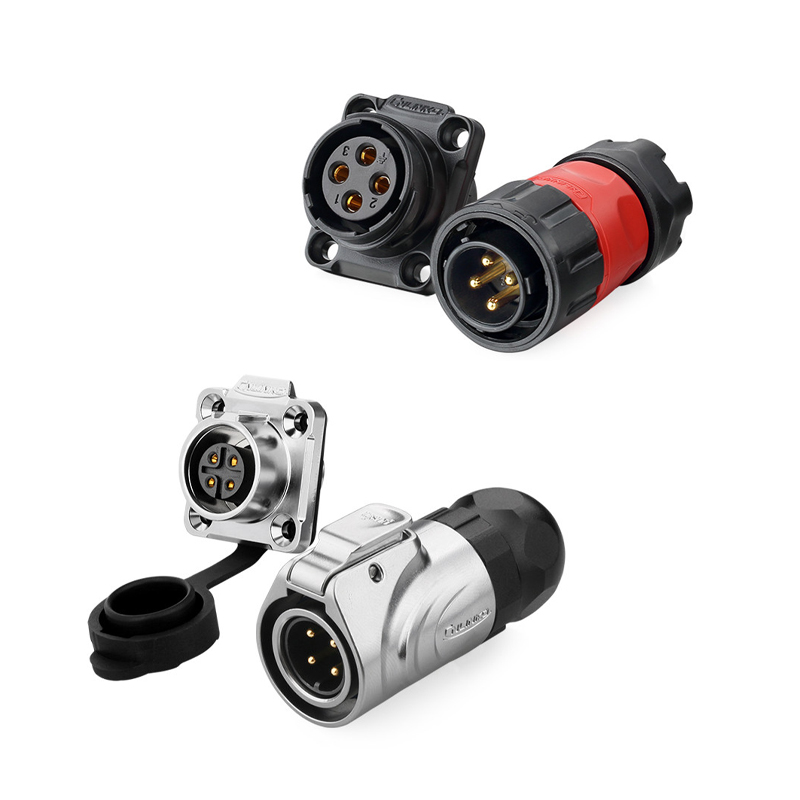
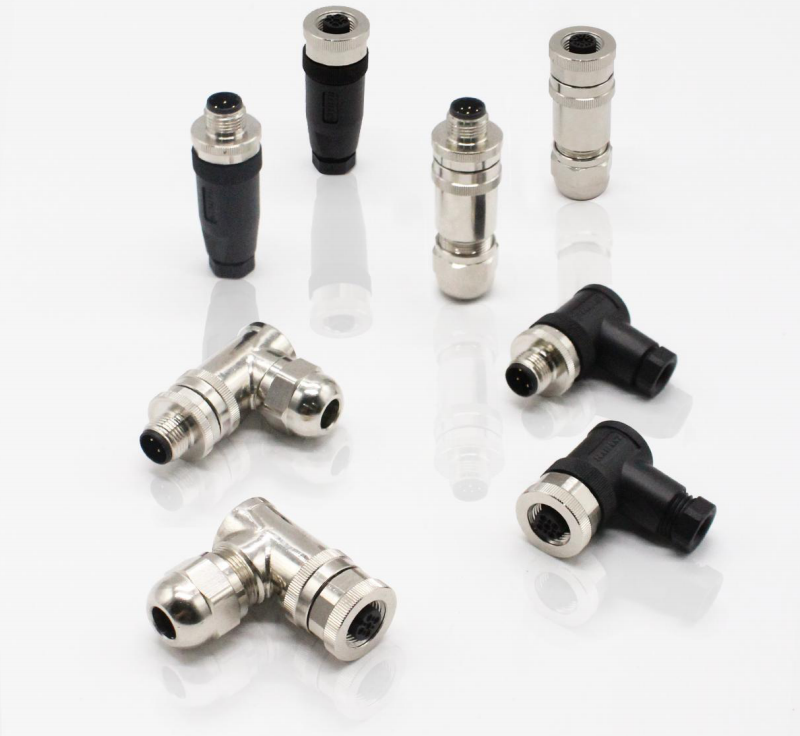
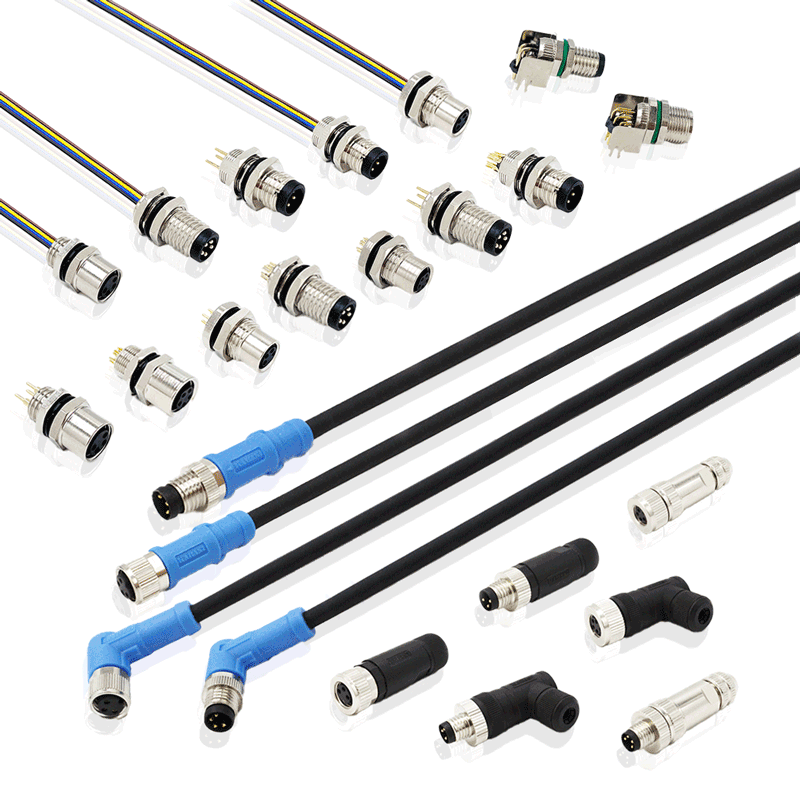
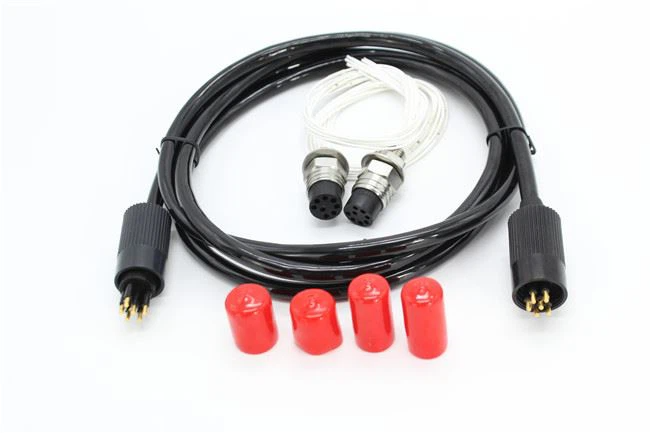
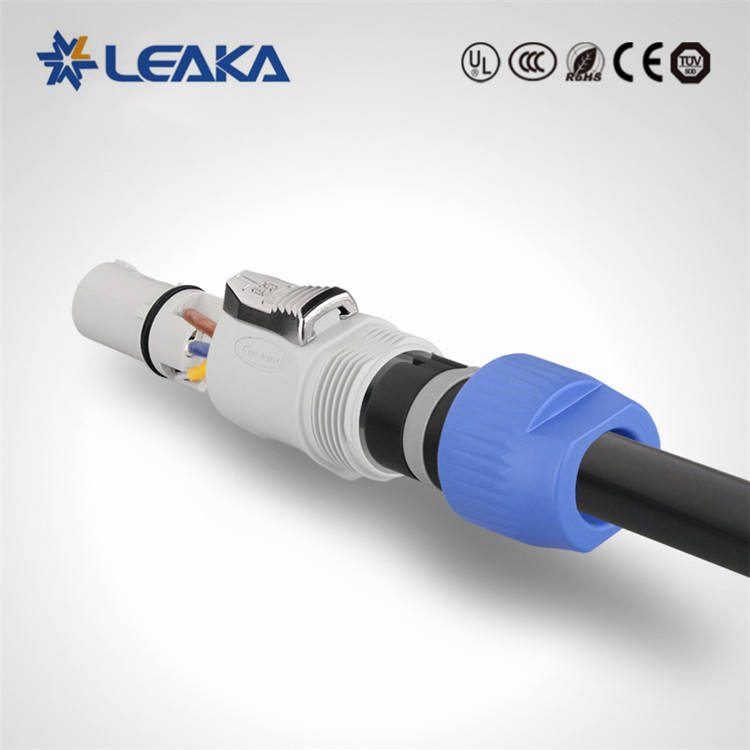
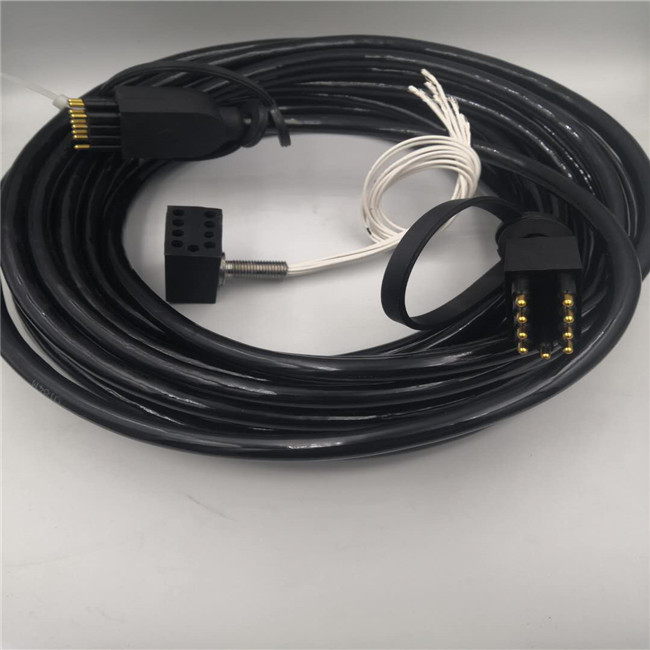
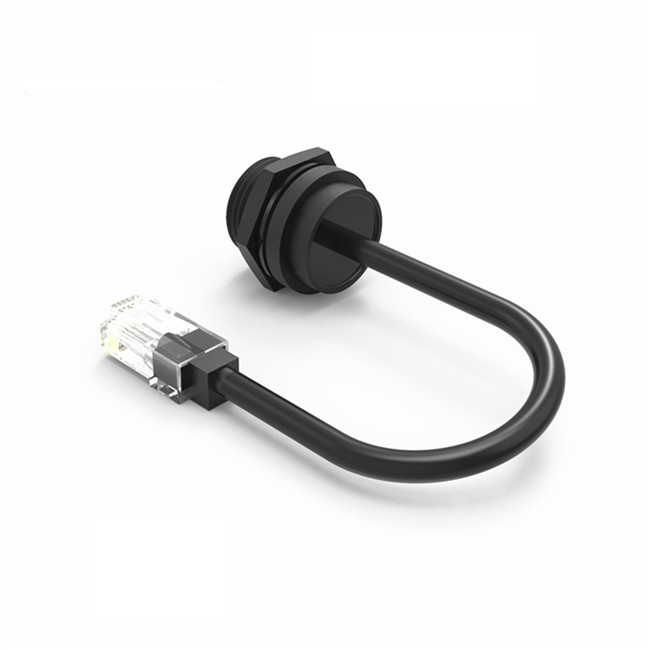
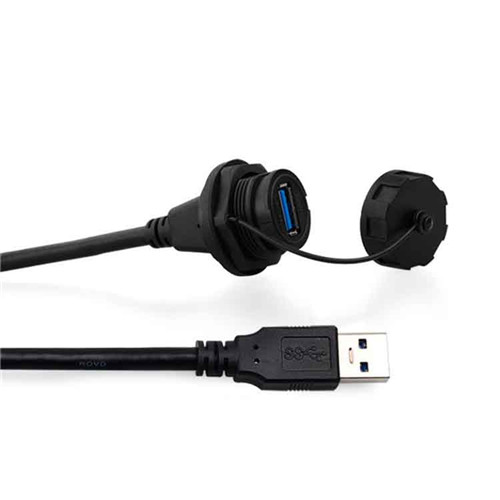
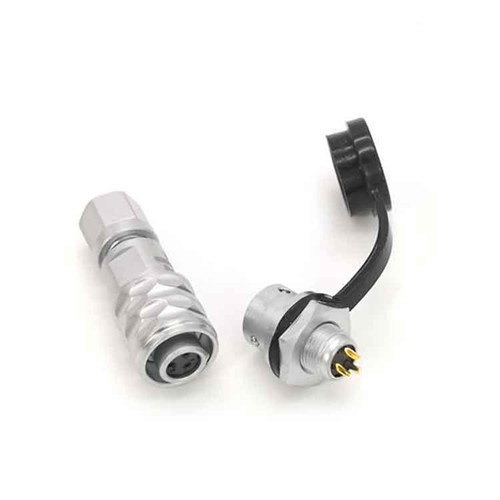
Terminal Block
Terminal Block
In the realm of electrical engineering and industrial applications, terminal blocks stand as indispensable components facilitating the organization, connection, and distribution of electrical circuits. These modest yet crucial devices serve as junction points, where wires converge to establish electrical connections within a system. Despite their apparent simplicity, terminal blocks play a multifaceted role, offering reliability, flexibility, and ease of maintenance in various settings, from domestic wiring to complex industrial machinery.
 Terminal block is an accessory product used to realize electrical connection, which is divided into the category of connector in industry.
Terminal block is an accessory product used to realize electrical connection, which is divided into the category of connector in industry.
With the increasing degree of industrial automation and the stricter and more precise requirements of industrial control, the amount of terminal blocks is gradually increasing.
With the development of the electronics industry, the use of terminal blocks is increasing, and there are more and more types. In addition to PCB board terminals, the most widely used ones are hardware terminals, nut terminals, spring terminals and so on.
1. Introduction to Terminal Blocks:
At its core, a terminal block is a modular, insulated block with metal clamps or screws, designed to secure and connect multiple wires or conductors. Its primary function is to terminate or connect electrical circuits, providing a safe and organized platform for managing wires within a system. Terminal blocks come in diverse shapes, sizes, and configurations, tailored to meet specific application requirements.
2. Components and Structure:
Terminal blocks typically consist of several key components:
Base: The foundational component of the terminal block, usually made of insulating material such as plastic or ceramic. It houses the metal conductive elements and provides mechanical support and electrical insulation.
Metal Clamps or Screws: These are the conductive elements mounted on the base, responsible for securing the wires or conductors in place. The clamps or screws may be made of materials like brass or stainless steel, ensuring conductivity and durability.
Marking System: Many terminal blocks feature a labeling or marking system, enabling users to identify connections easily. This could include numerical labels, color-coding, or other indicators for efficient troubleshooting and maintenance.
3. Types of Terminal Blocks:
Terminal blocks come in various types, each suited to specific applications:
Barrier Terminal Blocks: These feature a barrier between each screw terminal, providing additional safety by preventing accidental contact between adjacent conductors.
DIN Rail Terminal Blocks: Designed to be mounted on DIN rails, these terminal blocks are widely used in industrial control panels and electrical cabinets, offering easy installation and maintenance.
PCB Terminal Blocks: These are directly mounted onto printed circuit boards (PCBs), facilitating the connection of wires or components to the board.
Feed-Through Terminal Blocks: These allow wires to pass through, enabling connections on both sides of the block, making them suitable for daisy-chaining or bridging circuits.
4. Applications of Terminal Blocks:
Terminal blocks find applications across various industries and domains:
Industrial Automation: In industrial automation systems, terminal blocks play a crucial role in connecting sensors, actuators, and control devices to PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) or other control units.
Power Distribution: Terminal blocks are used for distributing power within electrical panels or cabinets, allowing multiple circuits to be connected to a single power source.
Building Wiring: In residential and commercial buildings, terminal blocks are utilized for organizing and connecting electrical wires, ensuring safe and reliable electrical distribution.
Transportation: Terminal blocks are employed in vehicles, trains, and aircraft for managing electrical connections in systems such as lighting, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), and control panels.
5. Advantages and Considerations:
Terminal blocks offer several advantages:
Modularity: Their modular design allows for easy expansion or modification of electrical systems without the need for extensive rewiring.
Accessibility: Terminal blocks provide easy access to individual connections, simplifying troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
Safety: With proper insulation and design, terminal blocks enhance electrical safety by reducing the risk of short circuits and electrical hazards.
However, there are also considerations to bear in mind:
Temperature Ratings: Terminal blocks should be selected based on their temperature ratings to ensure compatibility with the operating environment and prevent overheating or melting.
Voltage and Current Ratings: It's essential to choose terminal blocks with appropriate voltage and current ratings to prevent overload and ensure reliable operation.
Environmental Conditions: Terminal blocks used in outdoor or harsh environments may require additional protection against moisture, dust, and other contaminants.
In conclusion, terminal blocks serve as indispensable components in electrical systems, providing a secure, organized, and reliable means of connecting wires and conductors. From industrial automation to building wiring, their versatility and functionality make them essential for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, terminal block designs will likely become more sophisticated, offering increased efficiency, connectivity, and integration with smart systems. Understanding the various types, components, and considerations associated with terminal blocks is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety in electrical installations.
In conclusion, terminal blocks serve as indispensable components in electrical systems, providing a secure, organized, and reliable means of connecting wires and conductors. From industrial automation to building wiring, their versatility and functionality make them essential for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, terminal block designs will likely become more sophisticated, offering increased efficiency, connectivity, and integration with smart systems. Understanding the various types, components, and considerations associated with terminal blocks is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety in electrical installations.
 Terminal block is an accessory product used to realize electrical connection, which is divided into the category of connector in industry.
Terminal block is an accessory product used to realize electrical connection, which is divided into the category of connector in industry.With the increasing degree of industrial automation and the stricter and more precise requirements of industrial control, the amount of terminal blocks is gradually increasing.
With the development of the electronics industry, the use of terminal blocks is increasing, and there are more and more types. In addition to PCB board terminals, the most widely used ones are hardware terminals, nut terminals, spring terminals and so on.